Apramycin (nebramycin II) is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used in veterinary medicine. It is produced by Streptomyces tenebrarius.
Medical uses
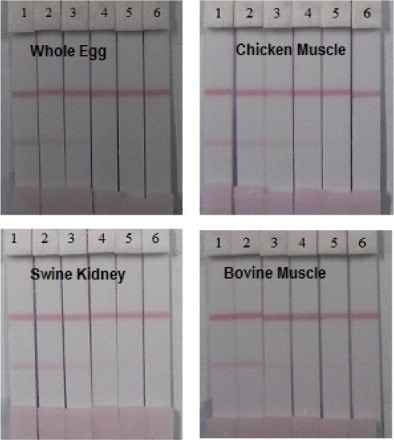
Apramycin can be used to treat bacterial infections in animals caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The following shows susceptibility data on medically significant organisms:
- Escherichia coli - 1 μg/mL - >512 μg/mL (this large range may be due to resistant organisms, typical MIC values are likely in the range of 2 -8 μg/mL.
- Klebsiella pneumoniae - 2 μg/mL - >256 μg/mL
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa - 4 μg/mL
Mechanism of action
Traditional knowledge suggests that aminoglycosides bind to the bacterial ribosome, leading to misreading of mRNA and incorporation of incorrect amino acids in the nascent polypeptide chain. However, aminoglycosides, including apramycin, have been shown to not only cause misreading of the genetic code but also significantly slow down the overall rate of protein synthesis in live bacterial cells. This dual effect on both accuracy and efficiency of protein synthesis helps to explain the bactericidal properties of apramycin.
References